When creating hydraulic models using the Hydrologic Engineering Center’s River Analysis System (HEC-RAS), most users rely on the user interface to assemble information correctly. However, it can be helpful to understand the file types that make up an HEC-RAS project. This is because understanding these file types can help modelers more easily understand how a model is set up (which is useful as projects become larger and more complex). Understanding the HEC-RAS file structure is also helpful when using the HEC-RAS Controller.
The following table summarizes the purpose of the HEC-RAS file types that make up a project.
| File Extension | Description |
|---|---|
| .B01 to .B99 | Boundary condition file for each unsteady flow plan run by the user. This file is created after running an unsteady flow model. |
| .BCO01 to BCO99 | Unsteady flow log output file generated for each unsteady flow plan run by the user. |
| .C01 to .C99 | Geometric pre-processor output file for unsteady flow models. This file is created after running an unsteady flow model. |
| .COLOR_SCALES | Contains the hydraulic color scale index, the water quality color scale index, and the sediment color scale index. |
| .COMP_MSGS.TXT | Generated for each model run in HEC-RAS. Contains the messages shown in the computation window during and after a model run. |
| .DSS | The Hydrologic Engineering Center’s Data Storage System (DSS) is a file type that allows for information to be easily shared/transferred between various HEC programs such as HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS. |
| .F01 to .F99 | Steady flow files |
| .G01 to .G99 | Geometry data files |
| .G01.HDF to .G99.HDF | Hierarchical Data Format (HDF5) file that corresponds to each geometry data file created |
| .H01 to .H99 | Hydraulic design data |
| .LOG | Log file generated for a model run |
| .IC.O01 to .IC.O99 | Initial conditions file generated for each unsteady flow plan run by the user. |
| .O01 to .O99 | Output data files |
| .P01 to .P99 | Plan data files |
| .P01.BLF to .P99.BLF | A binary log file is generated for each plan run by the user. This file is for the user interface. |
| .PRJ | Project file containing general information about the HEC-RAS Project |
| .Q01 to .Q99 | Quasi-unsteady flow file |
| .R01 to .R99 | Run files |
| RASEXPORT.SDF | File format used for importing and exporting geometry data |
| .RASMAP | Contains information about the different files shown in RAS Mapper |
| .RST | Restart (Hot Start) file generated (if the option is turned on by the user) for the purpose of establishing initial conditions. |
| .U01 to .U99 | Unsteady flow files |
| .S01 to .S99 | Sediment data |
| .SED01 to .SED99 | Sediment output files are created as intermediate files when a sediment transport model is run. |
| .SEDCAP01 to .SEDCAP99 | Sediment transport capacity data |
| .SEDHEADXS01 to .SEDHEADXS99 | Header files for sediment cross-section output are created as intermediate files when a sediment transport model is run. |
| .SEDXS01 to .SEDXS99 | Sediment cross-section output files are created as intermediate files when a sediment transport model is run. |
| .X01 to .X99 | Unsteady flow analysis run file |
The file types shown in the table will be described in further detail below.
General
.PRJ
The project file contains general information about the HEC-RAS model such as plan names, geometry files, flow files, and units (see the image below). Take care not to confuse a project file with a projection file (.prj), which is used to set the projection of a file in RAS Mapper. Refer to this blog post if you would like to learn more about projection files.

.COLOR_SCALES
This file contains information about color scales.

.DSS
The Hydrologic Engineering Center’s Data Storage System (HEC-DSS) can be used to share information between HEC programs such as HEC-HMS, HEC-RAS, or HEC-MetVue. Unlike many of the other file types discussed in this blog post, DSS files will not make any sense if you attempt to open them in NotePad or some other text viewer. Fortunately, HEC-RAS has a DSS viewer that can be accessed by navigating to the main menu and clicking View –> DSS Data. The following window will appear.
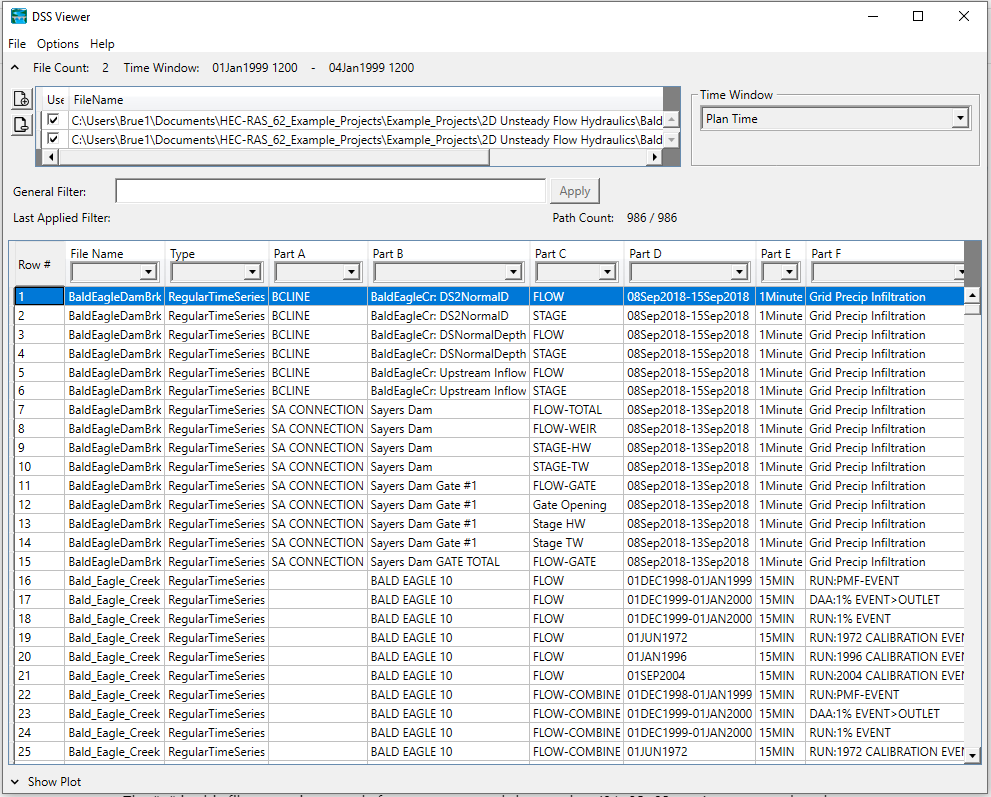
A .DSS file is automatically generated as an output when you run an unsteady flow model. This file contains time series data that is viewable by any program that can read .DSS files. If your HEC-RAS model links to a .DSS file to access input data such as an inflow hydrograph, know that .DSS file will be necessary to run your HEC-RAS model. For this reason, it is important to remember to include all input .DSS files when sending your model to a colleague or reviewer.
.RASMAP
A .rasmap file contains information about the different files shown in RAS Mapper.

Geometry Files
.G01 to .G99
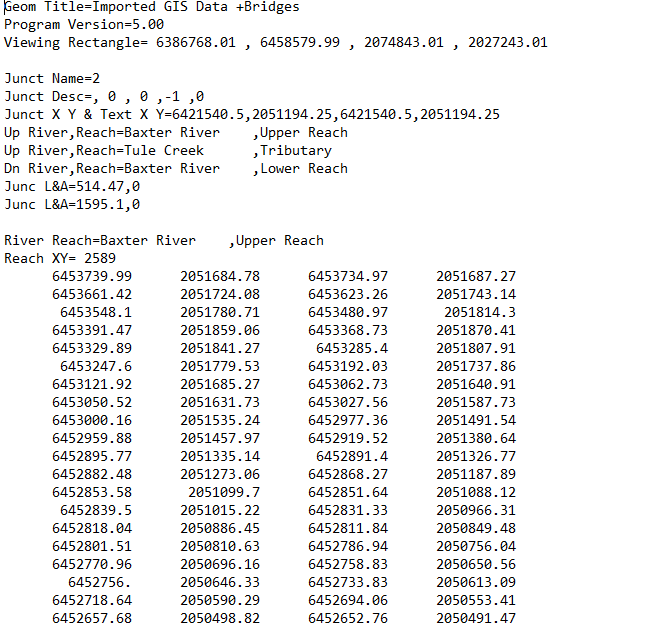
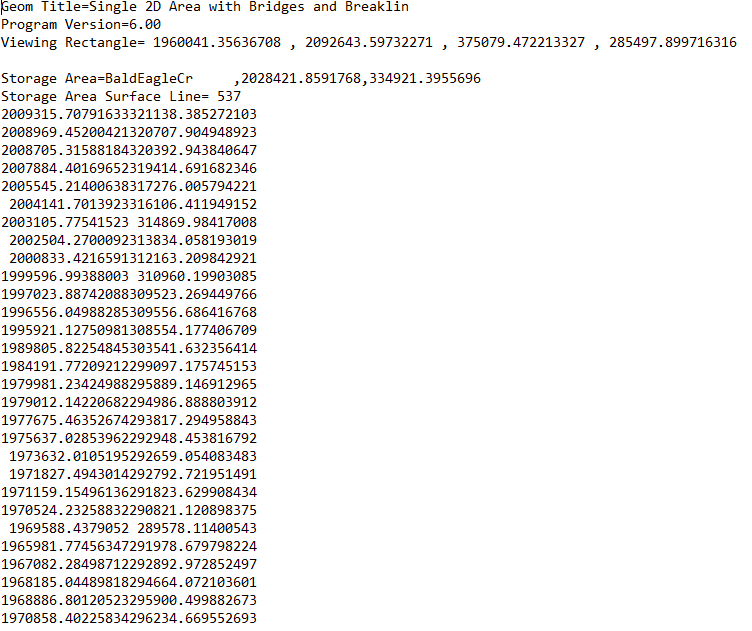
The “g” in this file extension stands for geometry, and the number (01, 02, 03, etc.) corresponds to the order in which they are saved. The geometry data are stored in an ASCII format, which means you can open them in NotePad and read the contents easily. You will see that the geometry files contain information about reaches, cross sections, junctions, hydraulic structures, storage areas, and other components that make up the geometry of your hydraulic model. HEC-RAS allows users to generate up to 99 geometry files. The screenshots below show how a 1D and 2D geometry file differ.
.G01.HDF to .G99.HDF
For each geometry file (.g01 to .g99), a corresponding Hierarchical Data Format (HDF5) file is generated. These files are used in RAS Mapper.
RASEXPORT.SDF
An SDF, which stands for Spatial Data Format, the file can be used to import and export geometric data. The HEC-RAS SDF format is an ANSI text file as shown in the image below. Although an HEC-RAS SDF file exported from HEC-RAS can be imported into AutoCAD Civil 3D, it is worth noting that an HEC-RAS SDF file is NOT the same as an Autodesk SDF file (which is more of an SQLite format rather than ANSI text).
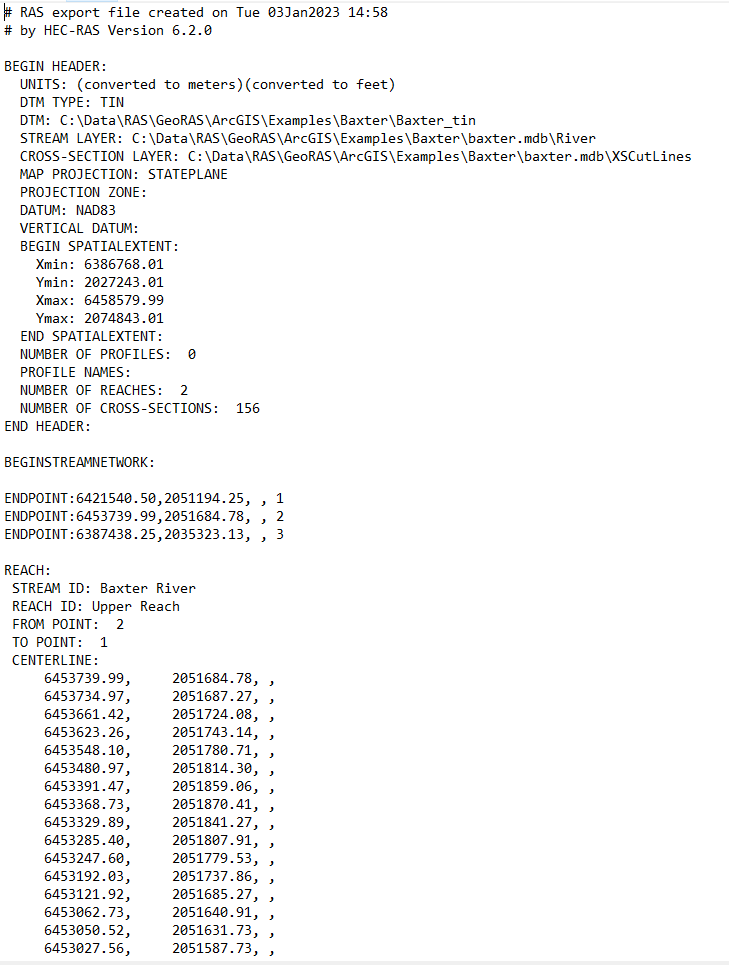
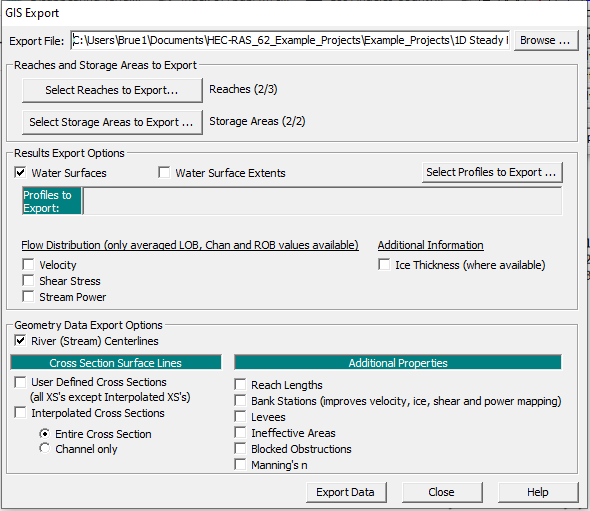
To export geometric data to a RASexport.sdf file, navigate to the main menu (not the Geometric Data Editor) and click File –> Export GIS Data. The following window will appear. Make the appropriate selections and click Export Data.
To import geometric data in a RASexport.sdf file, navigate to the Geometric Data Editor and create a new geometry file. Then click File –> Import Geometry Data –> GIS Format. Finally, navigate to the applicable RASexport.sdf file and click Ok.
Flow Data
The following section describes flow data (e.g., steady flow, unsteady flow, and quasi-unsteady flow) files in an HEC-RAS project. The files used for flow data are stored in an ASCII format and can be viewed in a text editor like NotePad. For the most part, the information stored in these files is self-explanatory.
.F01 to .F99
Steady flow files are indicated by the .F01 to .F99 file extensions. The “F” indicates that the file is a steady flow file, and the number (01 to 99) corresponds to the order in which the steady flow files were saved. These files contain information about profiles, boundary conditions, and flow rates. A screenshot of a steady flow file is shown below.
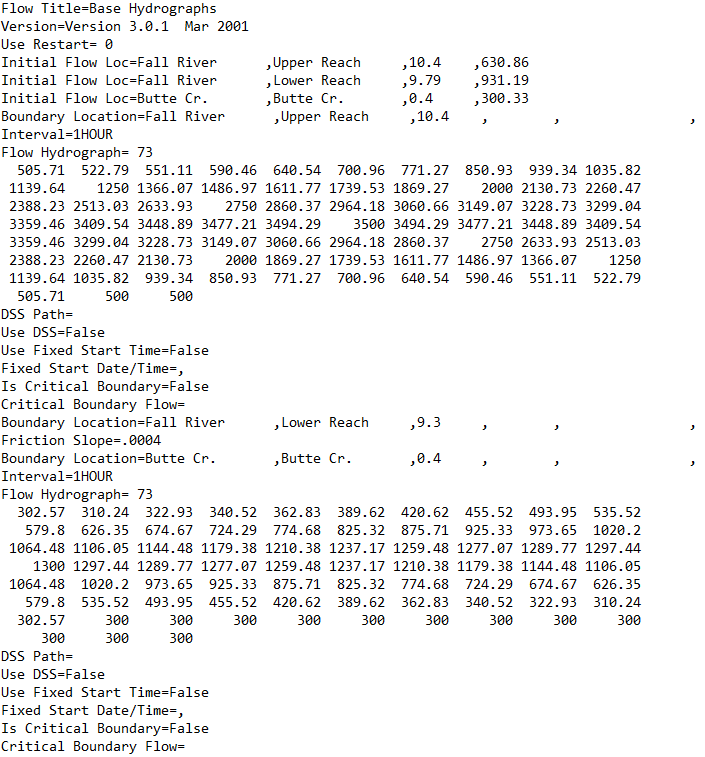
.U01 to .U99
Unsteady flow files are indicated by the .U01 to .U99 file extensions. The “U” indicates that the file is an unsteady flow file, and the number (01 to 99) corresponds to the order in which the unsteady flow files were saved. These files contain information about profiles, boundary conditions, and hydrographs. A screenshot of an unsteady flow file is shown below.
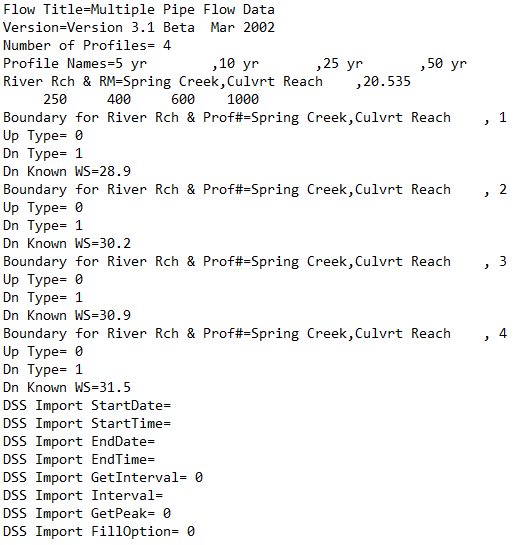
.Q01 to .Q99
Quasi-unsteady flow files are indicated by the .Q01 to .Q99 file extensions. The “Q” indicates that the file is an unsteady flow file, and the number (01 to 99) corresponds to the order in which the quasi-unsteady flow files were saved. This file includes information about boundary conditions, flow rates, and temperature. It is worth noting that quasi-unsteady flow data files are used for one-dimensional (1D) sediment transport analyses.

Unsteady Flow Output Files
After unsteady flow computations are performed by HEC-RAS, the program creates some additional files.
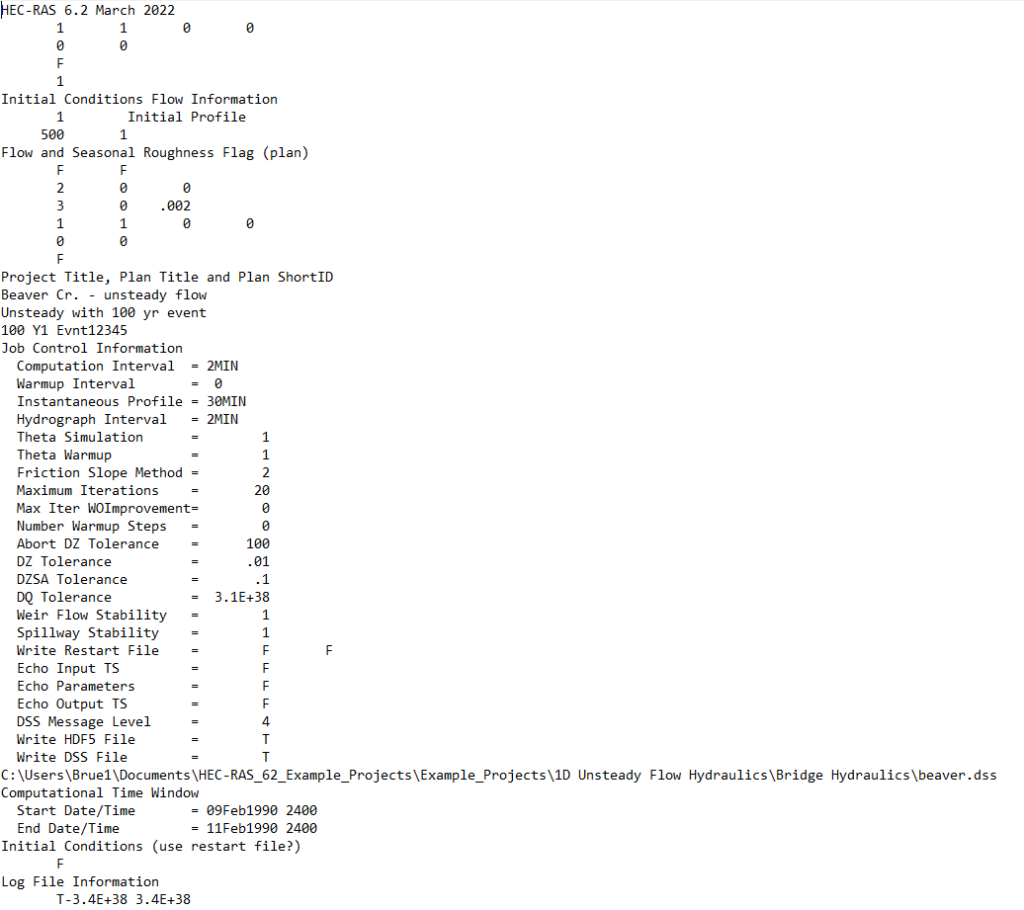
.B01 to .B99
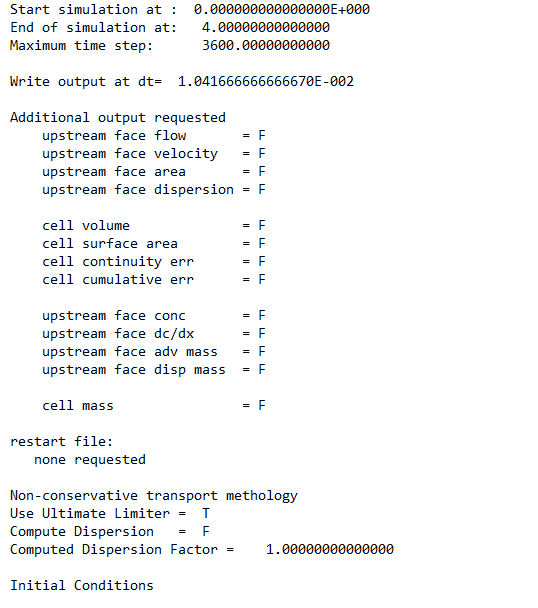
Boundary condition file for each unsteady flow plan run by the user. The following screenshot shows some of the information shown in the boundary condition file generated during an unsteady flow run.
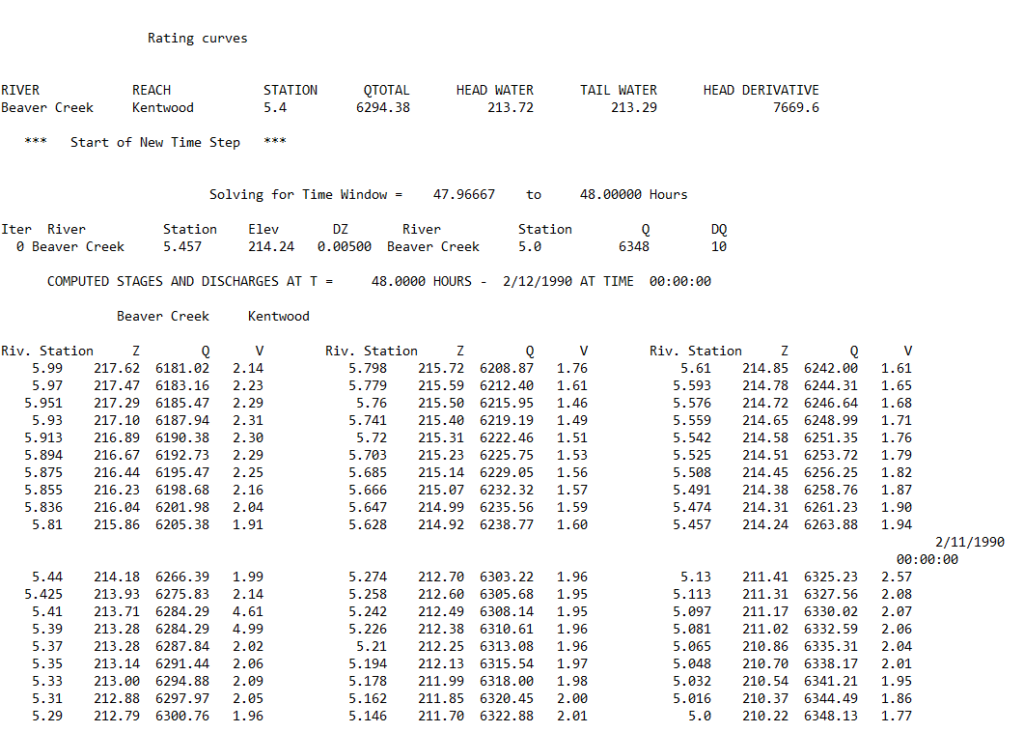
.BCO01 to .BCO99
The unsteady flow log output file contains information about the unsteady flow run including rating curves and the volume accounting error. This file can also be accessed by clicking Options –> View Computation Log File in the Unsteady Flow dialog box. Users can also adjust what is presented in the unsteady flow log output file by adjusting the settings by clicking Options –> Output Options in the Unsteady Flow dialog box. Then click the Log Output Options tab.
A screenshot of part of an unsteady flow log output file is shown below.
.C01 to .C99
The geometric pre-processor output files contain the hydraulic properties tables, rating curves, and family of rating curves for each cross-section, bridge, culvert, storage area, inline structure, and lateral structure. This file is rewritten each time you change your geometry file. It cannot be read in a text editor.
.IC.O01 to .IC.O99
An initial conditions file is generated for each unsteady flow plan run by the user.
.P01.BLF to .P99.BLF
A binary log file is generated for each plan run by the user. This file is for the user interface.
.RST
HEC-RAS will create a restart (Hot Start) file that corresponds to a particular unsteady flow plan if indicated by the user. A restart file can be used to establish initial conditions (see the Initial Conditions tab of the Unsteady Flow Data Editor) and can be useful in stabilizing models as it provides HEC-RAS with a “warm-up” before the simulation. To create a restart file, click Options –> Output Options. Then click on the Restart File Options tab as shown below.
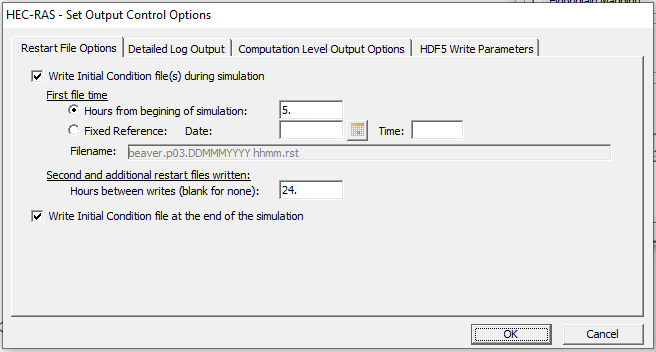
To learn more about restart files, check out this blog post from the RAS Solution blog.
Plan Files
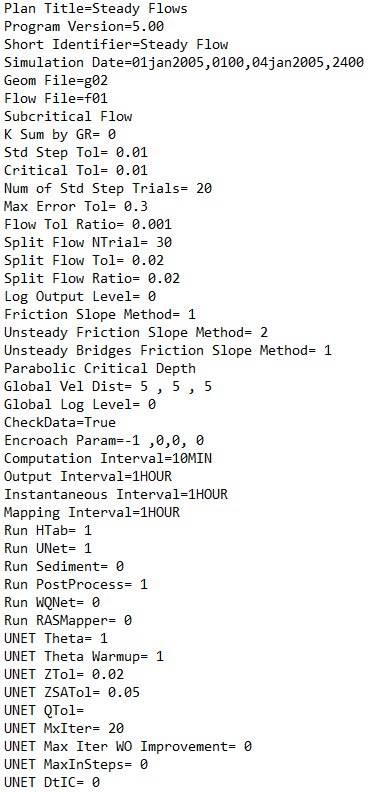
.P01 to .P99
The plan files contain information about the HEC-RAS plan being run. This includes information about the geometry file and flow information being used to run the model. It also contains information about various calculation and output settings applied to the model. A screenshot of a plan file is shown below.
Run Files
.R01 to .R99
The run files for steady flow analysis are created during an actual model simulation. It contains the information required to run the computational engine. A screenshot of a steady flow run file is shown below.

.X01 to .X99
The run files for unsteady flow analysis are created during an actual model simulation. It contains the information required to run the computational engine. A screenshot of an unsteady flow run file is shown below.
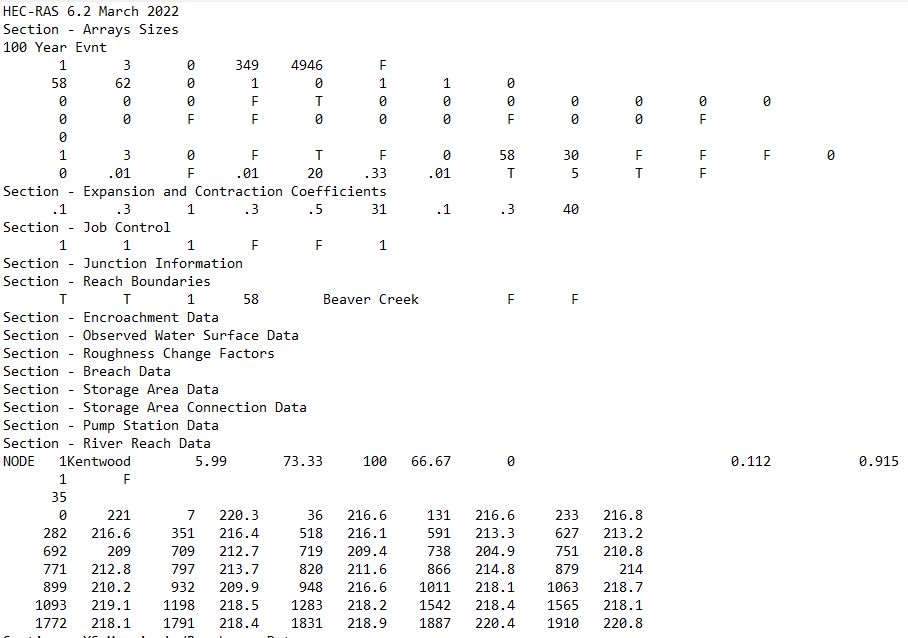
Output Files
.O01 to .O99
Output files are indicated by the .O01 to .O99 file extensions. The “O” indicates that the file is an output file, and the number (01 to 99) corresponds to the order of the plan files. For example, an output file with the extension .O15 is the output file that corresponds to the plan file with an extension .P15. Output files are written in a binary format and can only be read through the HEC-RAS user interface. If you try to open them in a text editor, it will not make sense.
.COMP_MSGS.TXT
A computational messages file is generated for each model run and contains the messages that are shown in the computation window after a model run. A screenshot of a computational messages file generated for an unsteady flow run is shown below.
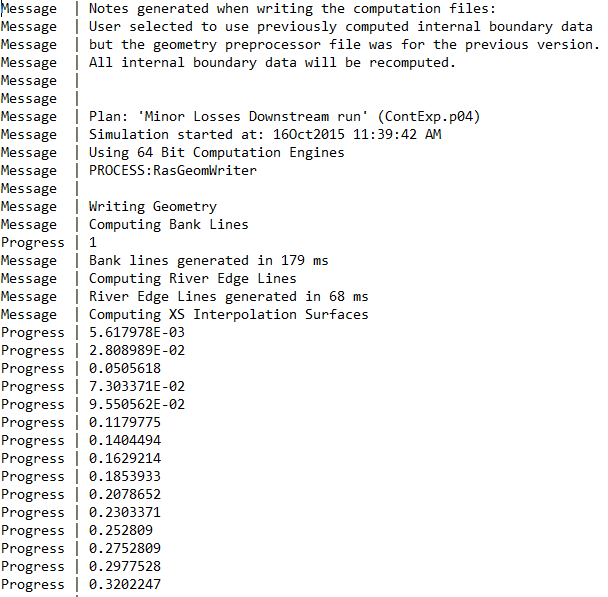
Sediment Files
.S01 to .S99
Sediment data files are indicated by the .S01 to .S99 file extensions. The “S” indicates that the file is a sediment data file, and the number (01 to 99) corresponds to the order in which the sediment data files were saved for a particular project. Sediment data files include flow data, boundary conditions for each reach, and sediment data. A screenshot of a sediment data file is shown below.
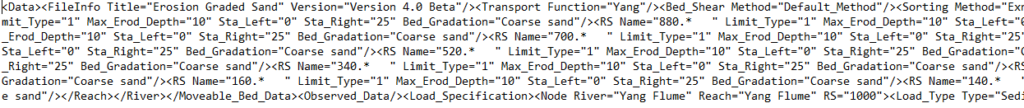
.SED01 to .SED99
Sediment output files are created as intermediate files when a sediment transport model is run.
.SEDHEADXS01 to . SEDHEADXS99
Header files for sediment cross-section output are created as intermediate files when a sediment transport model is run.
.SEDXS01 to .SEDXS99
Sediment cross-section output files are created as intermediate files when a sediment transport model is run.
Water Quality Files
.BC01 to .BC99
Water quality log files are created for each plan run. A screenshot of the water quality log file is shown below.
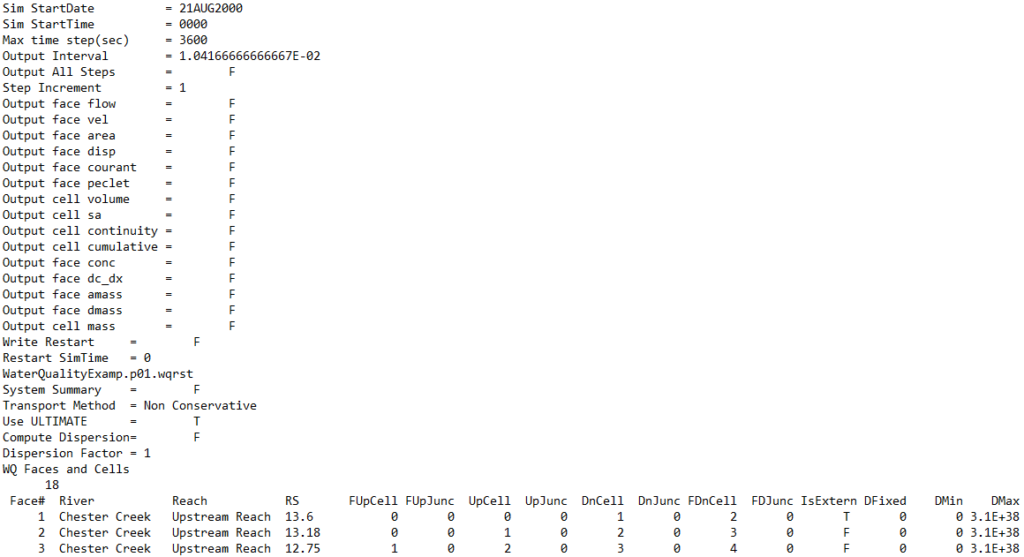
.P01.WQRST to .P99.WQRST
Water quality restart file.
.WQ_MSG01 to .WQMSG99
Water quality computational message text file (see screenshot below).